Mimetics Co., Ltd. (CEO Hyung-gi Park) participated as an industry–academic research partner in the development of a customizable double-layer adhesive patch capable of loading cosmetic and pharmaceutical agents, jointly conducted with the research team led by Professor Chang-Hyun Bang of the Department of Chemical Engineering at Sungkyunkwan University (President Ji-Beom Yoo).
The study was led by Min-Jin Kim and Min-Woo Song, Ph.D. candidates (co–first authors) from Professor Bang’s research group, who carried out the structural design and performance validation of the technology. Mimetics contributed as an industry partner by evaluating application feasibility and collaborating from a commercialization perspective.
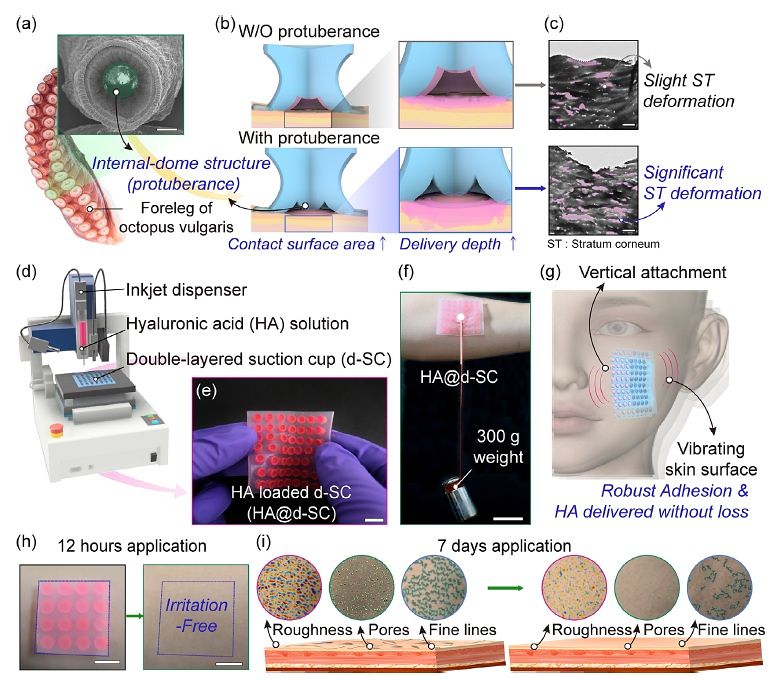
The research team drew inspiration from the distinctive dome-shaped internal protrusion structures found inside octopus suction cups. This biomimetic structure maximizes the skin contact area and generates strong negative pressure, temporarily deforming the stratum corneum to enhance transdermal drug penetration.
Conventional topical application methods often suffer from active ingredients flowing downward due to gravity, while sheet masks and conventional skin patches easily detach during movement, significantly limiting usability in daily life. To overcome these limitations, the team developed a customizable adhesive patch utilizing inkjet printing technology, enabling users to precisely and conveniently load desired active ingredients.
Patches precisely loaded with hyaluronic acid demonstrated exceptionally strong static adhesion, supporting a vertical load of up to 300 grams, and successfully delivered active agents without detachment even under intense vibration conditions reaching 3G (three times gravitational acceleration).
Notably, compared with conventional methods in which active ingredients tend to run off and exhibit poor skin absorption, the customizable adhesive patch achieved up to a tenfold increase in transdermal absorption even in vertical orientations, delivering active ingredients to depths of up to 202 micrometers into the skin. Furthermore, clinical testing involving daily application for 20 minutes over seven consecutive days confirmed statistically significant improvements compared with the control group.
Hyung-gi Park, CEO of Mimetics, stated,
“This research presents an innovative platform capable of stable drug delivery even under conditions involving perspiration, contoured skin surfaces, and vigorous movement. We anticipate broad expansion into diverse applications, including functional cosmetics and therapeutic patches that require continuous management during daily life.”
The joint research team plans to further advance the technology into a personalized healthcare solution by systematically analyzing delivery efficiency according to individual skin characteristics, including race, age, and gender.
This research was supported by the Mid-Career Research Program and the Pan-Government Regenerative Medical Technology Development Program funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea, as well as by Mimetics Co., Ltd. The study was published online in Advanced Functional Materials, a leading international journal in the field of materials science, in 2025.